Steyr Pinzgauer 6x6
Overview

The Pinzgauer is a family of high mobility vehicles (4x4 and 6x6) by Steyr. The vehicle was in serial production from 1971 till 2000 at Steyr. At that point, the production rights were transferred to the UK. Fist to Automotive Technik Ltd, later to BAE Systems. This vehicle is no longer in production.
The vehicle was designed primarily for army use. Some vehicles have been sold to rescue services and private owners. Given the high price of this specialised vehicle, only a very limited number of vehicles were sold new to private owners. Most of them drive an ex-army vehicle.
Table of contents

History
The vehicle was designed when Erich Ledwinka was the chief engineer. He and his father Hans Ledwinka used to work for Tatra, where Hans Ledwinka did pioneer the centre tube design and air-cooled engines (including a V8). Tatra does still use this centre tube design for its heavy off-road trucks.
Developed in the second half of the ‘60, the production started in 1971.
Design
Central tube
The Pinzgauer is designed around a central tube which houses the drive line. The engine and gearbox are mounted behind the front axle. The transfer case is mounted inside the tube, in front of the rear axle differential. Prop shafts without U-joints are mounted inside the tube and drive the front axle. (and the third axle of the 6x6) The front and rear tow hooks are connected to the tube. On top of this tube sits the chassis which supports the body.
Axles
The axles are solid beam half axles with portal reduction hubs. These half axles pivot around the differentials, which are mounted inside the tube. Each differential does have an electrically operated hydraulic differential lock.

Suspension
The 4x4 version does have coil springs all round. The 6x6 version uses coil springs on the front axle and a parabolic leaf spring at the rear to provide an even load distribution over the rear axles.
Engines
Erich Ledwinka is also credited for designing various air-cooled engines, including the engines for and the first generation Pinzgauer. The air-cooled engine in the first generation Pinzgauer is a 2.5L 4 cylinder. Later a 2.7 l, 76 kW (K-Jetronic injection) version became available. The later engine was mainly used in civilian ambulances. Like many other air-cooled engines, these engines do have a reputation for being loud. Especially inside an army vehicle without sound deafening.
Variants
The Pinzgauer 4x4 (710) and 6x6 (712) were available in different body styles. These included:
- soft top with lateral seats
- hard top with lateral seats
- hard top 5 door van crew cab
Second generation

The development of second-generation Pinzgauer started in 1980. It rolled off the production line in 1986. The version number for the 4x4 was 716 and 718 for the 6x6.
The main changes are:
- water-cooled turbo diesel engines from Volkswagen (2.4L 6 cylinder), the front of the vehicle is modified to house the radiator
- the standard use of an automatic ZF gearbox (a manual gearbox was an option)
- disk brakes
- a GVM upgrade
- slightly wider track
- slightly bigger tyres
Over the years, the second generation Pinzgauer did receive some small updates. (unlike the first generation). Internally these were called the P80 (original version), the P90 and P93. The P93 does have an updated engine with an intercooler.
Production in the UK

The British company Automotive Technik Ltd did acquire the production rights for the Pinzgauer in 2000. Their main customer was the British army.
The vehicles built by Automotive Technik Ltd did receive a new engine in 2003, to meet the EURO 3 emission standards. This is the 2.5L 5 cylinder TDI engine from Volkswagen.
The British vehicles doe also have a modified front, probably to make space for a larger radiator or the intercooler.
Automotive Technik Ltd did also offer an air suspension option on its Pinzgauer.
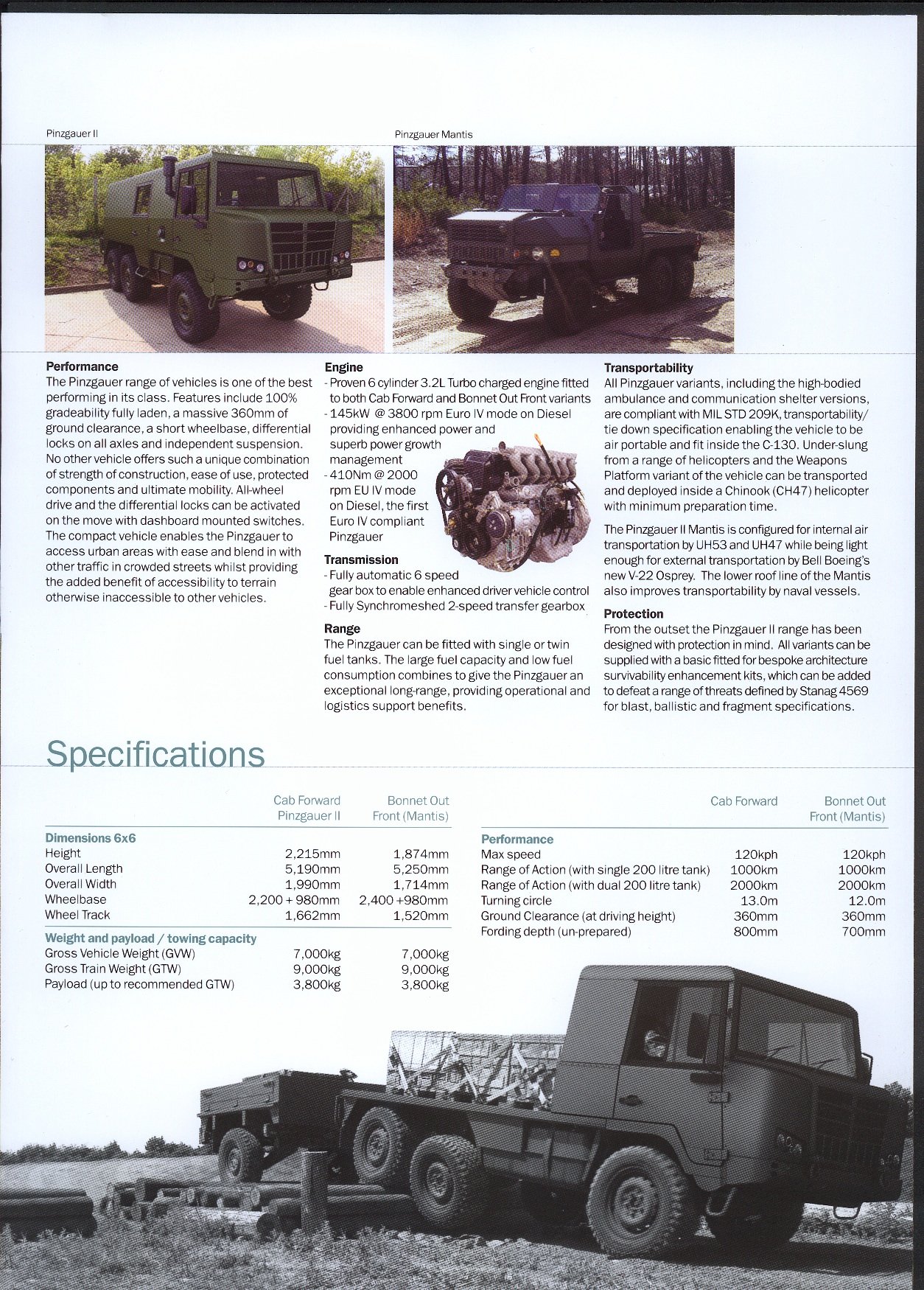
Pinzgauer II

The production rights for the vehicle ended up at BAE Systems in August 2007, after some acquisitions.
BAE Systems did showcase an updated version of the Pinzgauer in September 2007, the Pinzgauer II. The vehicle is larger and does have a higher GVM. The development did include a 4x4, a 6x6 and even an 8x8 version. An armour kit was also developed. The prototypes shown are all 6x6 vehicles.
The production of the Pinzgauer ended in 2008 due to a lack of sales.
Pinzgauer II Mantis

One big change was the addition of the Pinzgauer Mantis to the line-up. This vehicle does have a traditional bonneted cab, the engine is mounted on top of the front axle.
Due to its design, the Mantis is lower and can be transported inside the CH-47 Chinook and UH-53 helicopters. The bonneted design should also offer additional protection against mines and it’s easier to access the engine. The downside of this design is the reduction of the cargo area. The 6-wheel drive makes it a good towing vehicle.
Advanced Vehicle Systems inc did subcontract on the design of the Mantis.
Engine
The engine in the Pinzgauer II is a 3.2L 6-cylinder turbo diesel engine from Steyr (!). The original Steyr company does not exist anymore, the engine is produced in Austria in one of the parts of the former group.
Specifications
Pinzgauer 712
- engine: air cooled 2.5L 4 cylinder, 62 kW - 66 kW, carburettor
- Lenght: 4950 mm
- Width: 1790 mm
- Height: 2045 mm
- GVM: 3500-3900 kg
- Climbing ability: 100%
Pinzgauer 718
- engine: VW 2.4L 6 cylinder turbo diesel
- Length 5308 mm
- Width: 1800 mm
- Height: 2160 mm
- GVM: 5000 kg
- Climbing ability: 80%
Pinzgauer 718 2003 UK
- Engine: Volkswagen 5 cylinder 2.5 litre turbo diesel (Euro 3), 136 hp / 100kW @ 4,500rpm and 280Nm from 1,400 to 2,400rpm
- Gearbox: ZF 4 speed automatic, 5 manual option
- Tranfer case: ZF synchronised 2 speed (1.061:1 and 2.452:1)
Pinzgauer II
- engine: Steyr 194 hp, 3.2L 6 cylinder turbo diesel
- gearbox 6 speed automatic
- GVM: 7000 kg
- GCM: 9000 kg
Links
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pinzgauer_High-Mobility_All-Terrain_Vehicle
- https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Steyr-Puch_Pinzgauer
- https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Erich_Ledwinka
- pinzgauer UK at archive.org
- http://www.military-today.com/trucks/pinzgauer.htm
- http://www.military-today.com/trucks/pinzgauer_716_718.htm
- http://www.military-today.com/trucks/pinzgauer_2.htm
- http://www.advancedvehiclesystems.com/engineering.aspx
Gallery
Promotion video by Automotive Technik Ltd
Development of the Pinzgauer II Mantis
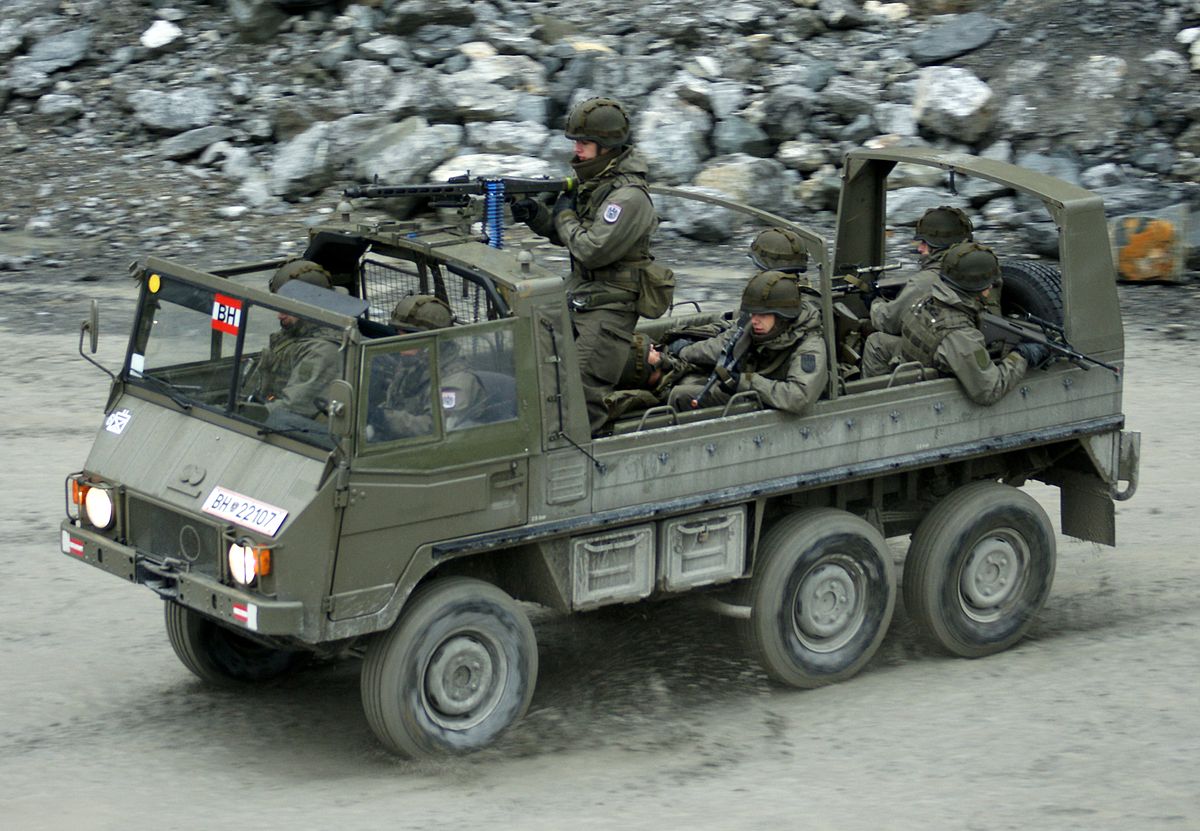 Pinzgauer 712 in service at the Austrian army, Picture credits: Wikimedia commons license
Pinzgauer 712 in service at the Austrian army, Picture credits: Wikimedia commons license
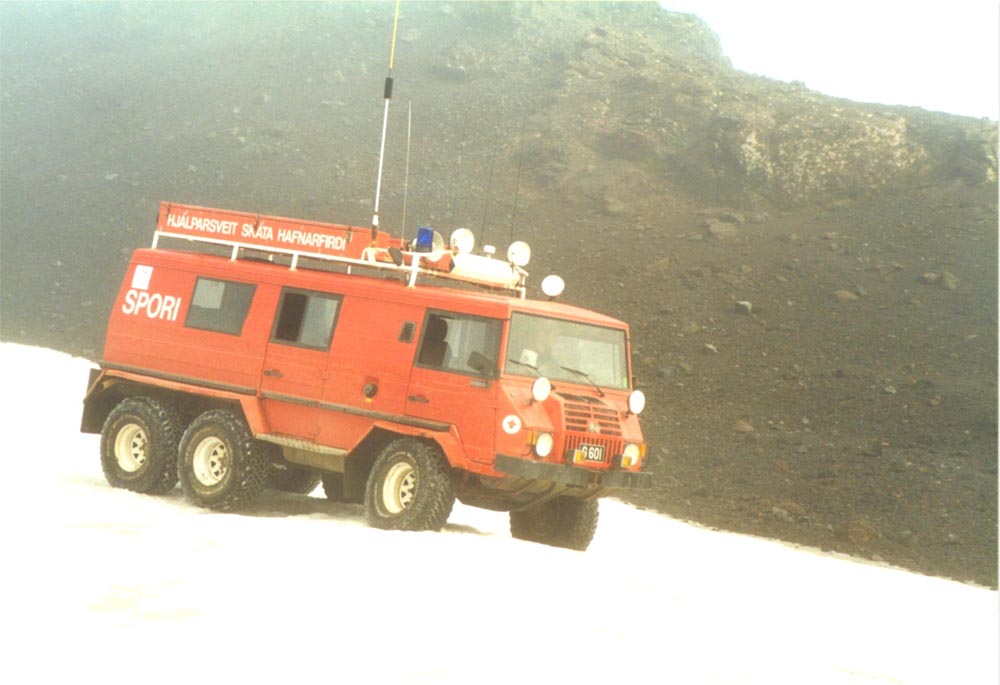 Pinzgauer 718, Picture credits: Automotive Technik Ltd
Pinzgauer 718, Picture credits: Automotive Technik Ltd
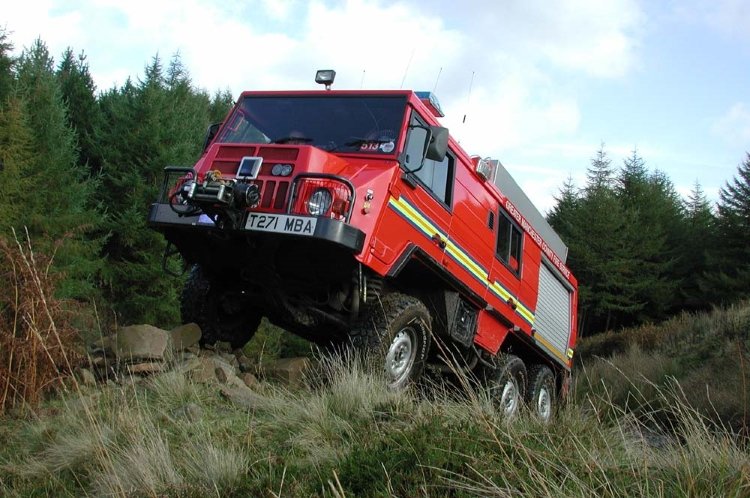 Pinzgauer 718 UK, Picture credits: Automotive Technik Ltd
Pinzgauer 718 UK, Picture credits: Automotive Technik Ltd
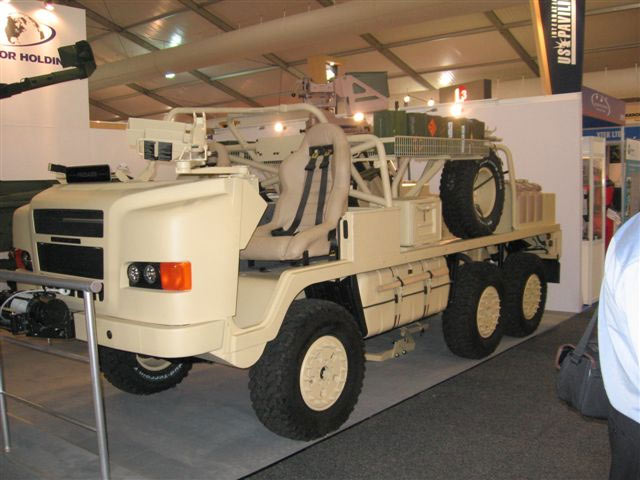

BAE Pinzgauer II 6x6
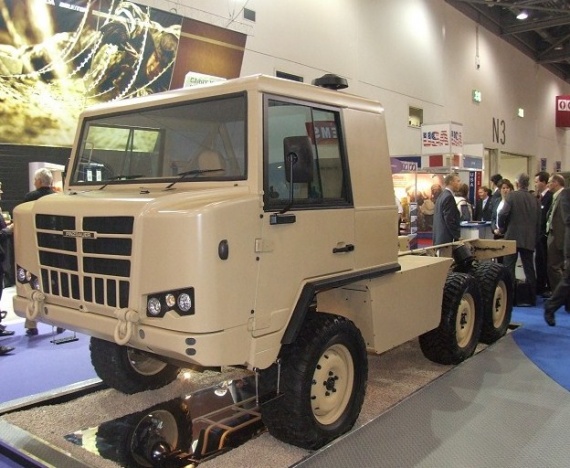

BAE Pinzgauer II 6x6

BAE Pinzgauer II Mantis 6x6
Pinzgauer II spec sheet